“most of data science is counting, and sometimes dividing” — Hadley Wickham
── Attaching packages ─────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse 1.3.2 ──
✔ ggplot2 3.4.0 ✔ purrr 1.0.1
✔ tibble 3.1.8 ✔ dplyr 1.1.0
✔ tidyr 1.3.0 ✔ stringr 1.5.0
✔ readr 2.1.4 ✔ forcats 0.5.2
── Conflicts ────────────────────────────────────────── tidyverse_conflicts() ──
✖ dplyr::filter() masks stats::filter()
✖ dplyr::lag() masks stats::lag()
count 函数功能就是统计某个变量在各组出现的次数。
<- tibble (name = c ("Alice" , "Alice" , "Bob" , "Bob" , "Carol" , "Carol" ),type = c ("english" , "math" , "english" , "math" , "english" , "math" ),score = c (60.2 , 90.5 , 92.2 , 98.8 , 82.5 , 74.6 )
# A tibble: 6 × 3
name type score
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Alice english 60.2
2 Alice math 90.5
3 Bob english 92.2
4 Bob math 98.8
5 Carol english 82.5
6 Carol math 74.6
# A tibble: 3 × 2
name n
<chr> <int>
1 Alice 2
2 Bob 2
3 Carol 2
count
%>% count (name,sort = TRUE ,wt = score,name = "total_score"
# A tibble: 3 × 2
name total_score
<chr> <dbl>
1 Bob 191
2 Carol 157.
3 Alice 151.
其中的 sort 是排序的方式,若TRUE,将升序排序;name将调整输出的列名。 wt若为一个变量,计算每组的和。
若不使用count(),我们也可以使用group_by() + summarise()来实现。
%>% group_by (name) %>% summarise ( n = n ())
# A tibble: 3 × 2
name n
<chr> <int>
1 Alice 2
2 Bob 2
3 Carol 2
同时我们可以在count中创建新变量:使用%>%传递参数,构建新变量
%>% count (range = 10 * (score%/% 10 ))
# A tibble: 4 × 2
range n
<dbl> <int>
1 60 1
2 70 1
3 80 1
4 90 3
add_count()来增加一列,代表每一个人参加的考试次数。
%>% group_by (name) %>% mutate (n = n ()) %>% ungroup ()
# A tibble: 6 × 4
name type score n
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <int>
1 Alice english 60.2 2
2 Alice math 90.5 2
3 Bob english 92.2 2
4 Bob math 98.8 2
5 Carol english 82.5 2
6 Carol math 74.6 2
# A tibble: 2 × 3
name type score
<chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 Bob english 92.2
2 Bob math 98.8
<- tribble (~ x, ~ y,1 , NA ,2 , NA ,NA , - 3 ,NA , - 4 ,5 , - 5
# A tibble: 5 × 2
x y
<dbl> <dbl>
1 1 NA
2 2 NA
3 NA -3
4 NA -4
5 5 -5
删除缺失数据:
# A tibble: 1 × 2
x y
<dbl> <dbl>
1 5 -5
summarise() 生成 list-column
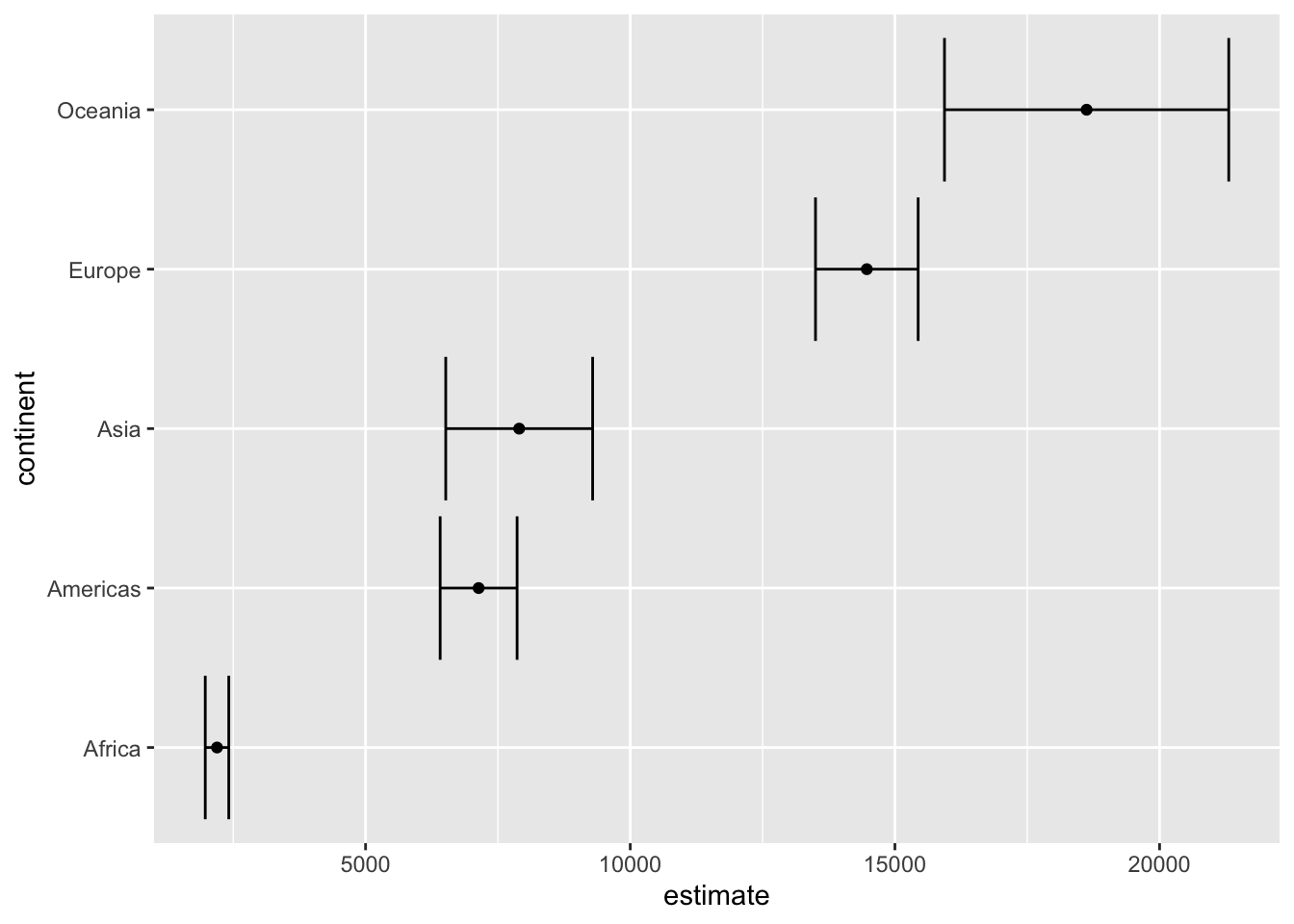
library (gapminder)%>% group_by (continent) %>% summarise (avg_gdpPercap = mean (gdpPercap)
# A tibble: 5 × 2
continent avg_gdpPercap
<fct> <dbl>
1 Africa 2194.
2 Americas 7136.
3 Asia 7902.
4 Europe 14469.
5 Oceania 18622.
%>% group_by (continent) %>% summarise (test = list (t.test (gdpPercap))) %>% mutate (tidied = purrr:: map (test, broom:: tidy)) %>% unnest (tidied) %>% ggplot (aes (estimate, continent)) + geom_point () + geom_errorbarh (aes (xmin = conf.low,xmax = conf.high
count() + fct_reorder() + geom_col() + coord_flip()
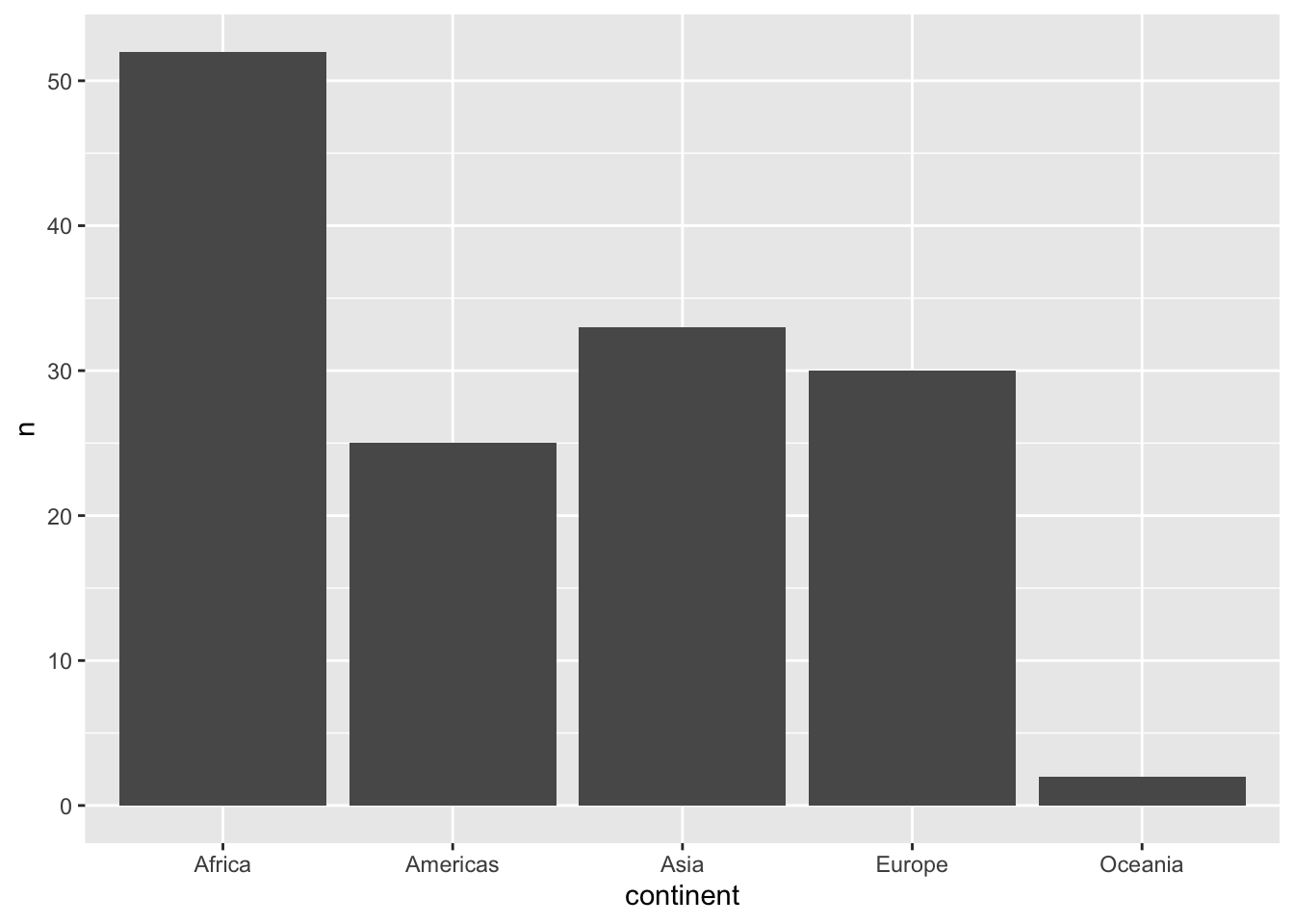
%>% distinct (continent,country)%>% count (continent)%>% ggplot (aes (x= continent,y= n))+ geom_col ()
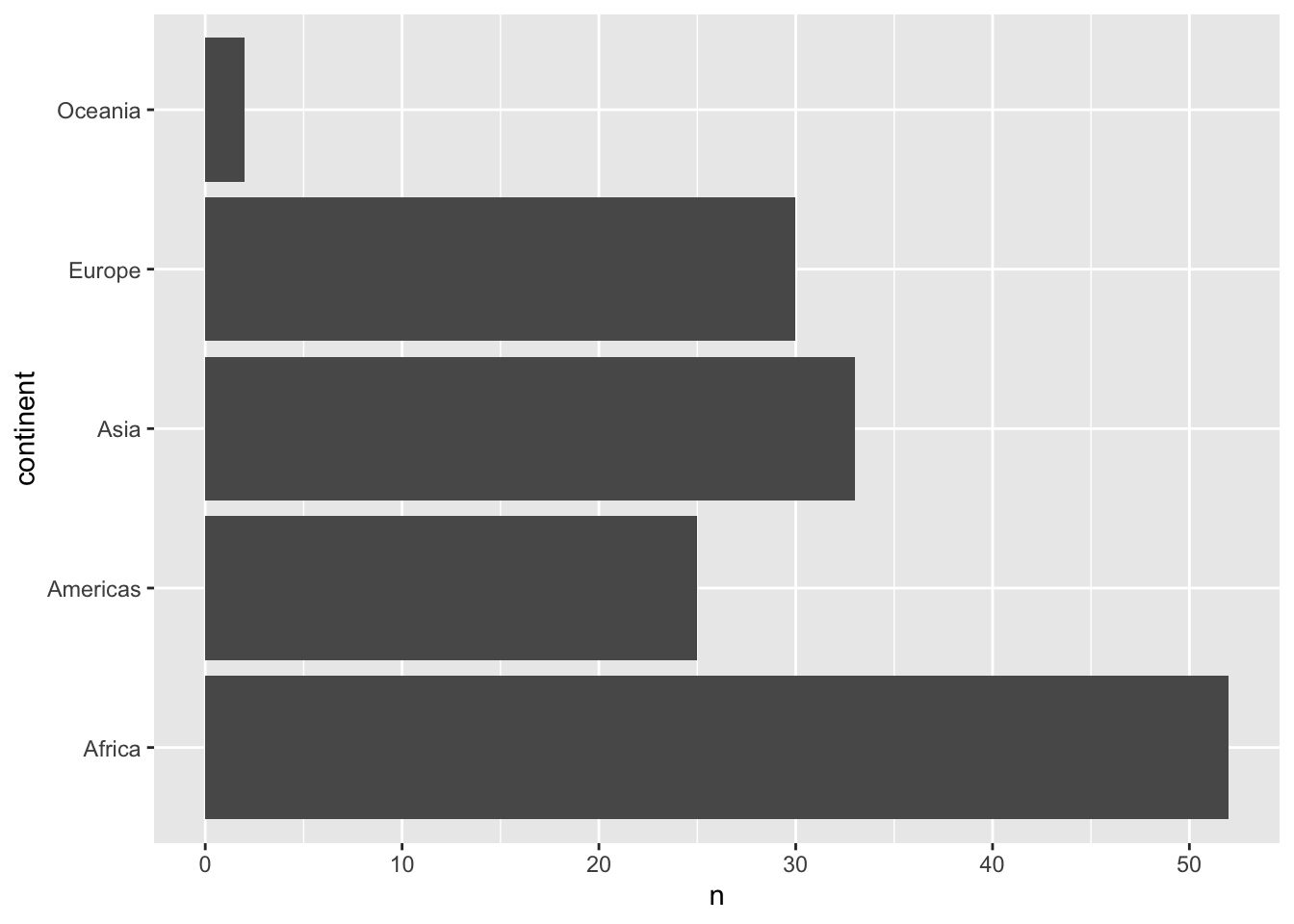
将其x转换到y轴:
%>% distinct (continent,country)%>% count (continent)%>% ggplot (aes (x= continent,y= n))+ geom_col ()+ coord_flip ()
distinct: keep only unique rows from a data frame.
%>% distinct (continent, country) %>% count (continent)
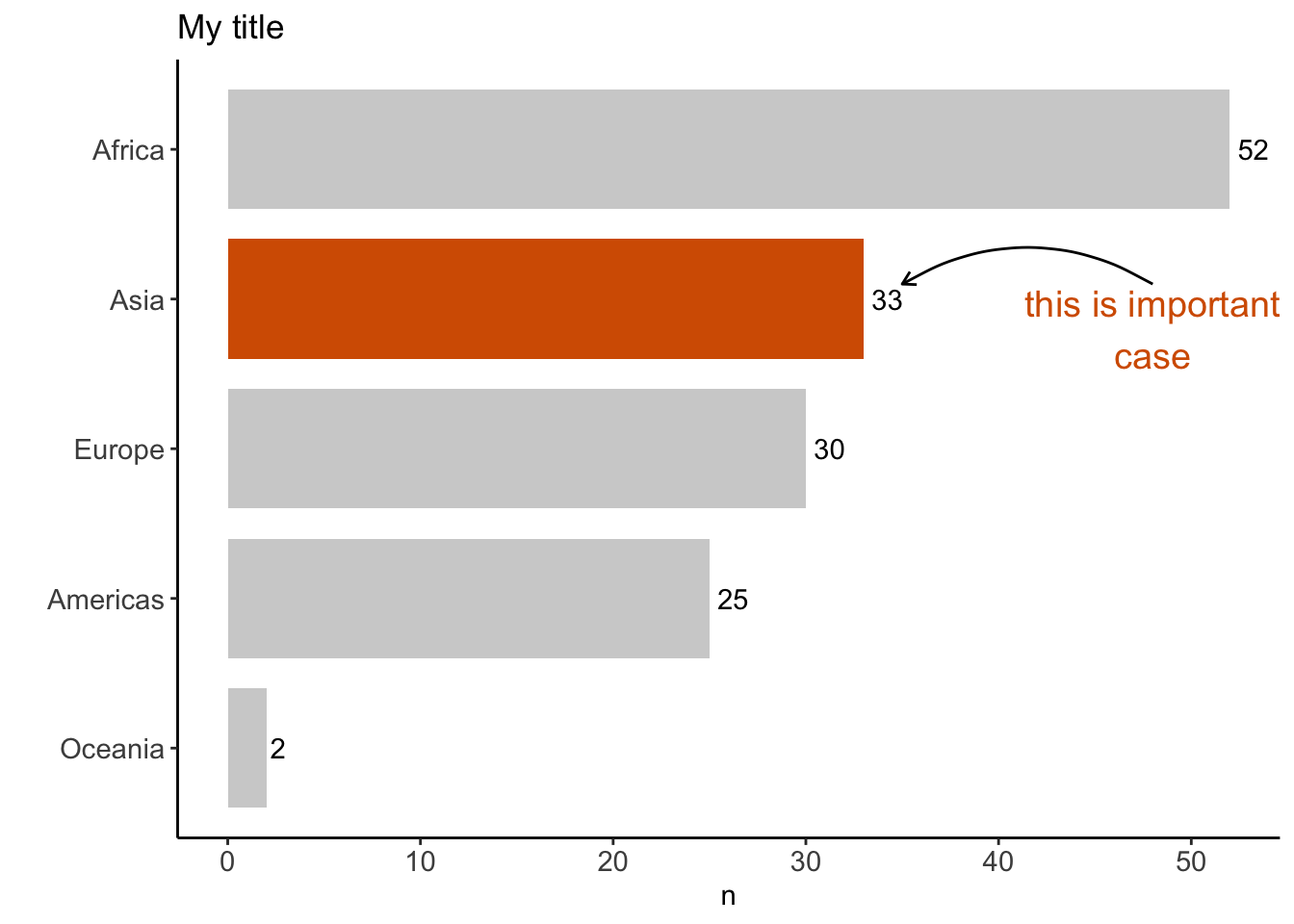
# A tibble: 5 × 2
continent n
<fct> <int>
1 Africa 52
2 Americas 25
3 Asia 33
4 Europe 30
5 Oceania 2
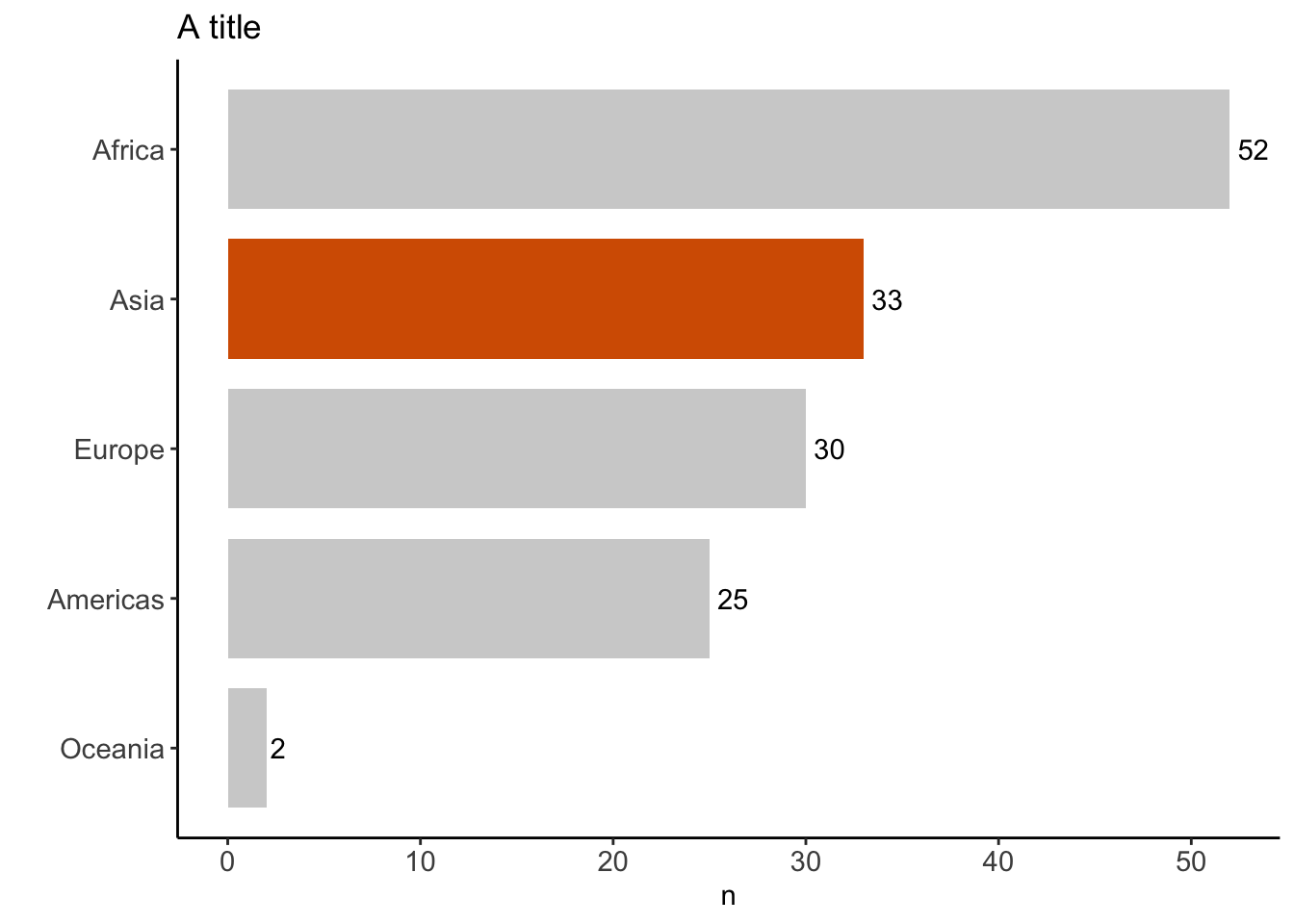
%>% distinct (continent, country) %>% count (continent)%>% mutate (coll = if_else (continent == "Asia" , "red" , "gray" )) %>% ggplot (aes (x = fct_reorder (continent, n), y = n)) + geom_text (aes (label = n), hjust = - 0.25 ) + geom_col (width = 0.8 , aes (fill = coll) ) + coord_flip () + theme_classic () + scale_fill_manual (values = c ("#b3b3b3a0" , "#D55E00" )) + theme (legend.position = "none" ,axis.text = element_text (size = 11 )+ labs (title = "A title" , x = "" )
添加annotate:
%>% distinct (continent, country) %>% count (continent) %>% ggplot (aes (x = fct_reorder (continent, n), y = n)) + geom_text (aes (label = n), hjust = - 0.25 ) + geom_col (width = 0.8 , aes (fill = continent == "Asia" ) ) + coord_flip () + theme_classic () + scale_fill_manual (values = c ("#b3b3b3a0" , "#D55E00" )) + annotate ("text" , x = 3.8 , y = 48 , label = "this is important \n case" , color = "#D55E00" , size = 5 ) + annotate (geom = "curve" , x = 4.1 , y = 48 , xend = 4.1 , yend = 35 , curvature = .3 , arrow = arrow (length = unit (2 , "mm" ))+ theme (legend.position = "none" ,axis.text = element_text (size = 11 )+ labs (title = "My title" , x = "" )
scoped()函数
对所有的列操作,使用_all;
对数据框指定的几列进行操作,可采用_at实现;
对数据框符合条件的几列进行操作,可以使用_if实现;
<- iris %>% as_tibble () <- iris %>% head (5 )
# A tibble: 5 × 5
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct>
1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa
2 4.9 3 1.4 0.2 setosa
3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa
4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa
5 5 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa
%>% mutate_if (is.double, as.integer)
# A tibble: 5 × 5
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species
<int> <int> <int> <int> <fct>
1 5 3 1 0 setosa
2 4 3 1 0 setosa
3 4 3 1 0 setosa
4 4 3 1 0 setosa
5 5 3 1 0 setosa
也可将函数写在list()中,使用purrr-style lambda形式写出
%>% mutate_if (is.numeric, list (~ scale (.), ~ log (.)))
# A tibble: 5 × 13
Sepal.Length Sepal.W…¹ Petal…² Petal…³ Species Sepal…⁴ Sepal…⁵ Petal…⁶ Petal…⁷
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa 1.16 0.850 0 NaN
2 4.9 3 1.4 0.2 setosa 0.193 -1.08 0 NaN
3 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa -0.772 -0.309 -1.41 NaN
4 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa -1.25 -0.695 1.41 NaN
5 5 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa 0.675 1.24 0 NaN
# … with 4 more variables: Sepal.Length_log <dbl>, Sepal.Width_log <dbl>,
# Petal.Length_log <dbl>, Petal.Width_log <dbl>, and abbreviated variable
# names ¹Sepal.Width, ²Petal.Length, ³Petal.Width, ⁴Sepal.Length_scale[,1],
# ⁵Sepal.Width_scale[,1], ⁶Petal.Length_scale[,1], ⁷Petal.Width_scale[,1]
我们使用slect加上_if就可以实现条件筛选变量:
<- tibble:: tibble (x = letters[1 : 3 ],y = c (1 : 3 ),z = c (0 , 0 , 0 )
# A tibble: 3 × 3
x y z
<chr> <int> <dbl>
1 a 1 0
2 b 2 0
3 c 3 0
%>% select_if (is.numeric)
# A tibble: 3 × 2
y z
<int> <dbl>
1 1 0
2 2 0
3 3 0
输入的为函数,同时都是作用在列上。
filter_if()函数
进一步的,我们还有filter_if:
<- ggplot2:: msleep%>% :: select (name, sleep_total) %>% :: filter (sleep_total > 18 )
# A tibble: 4 × 2
name sleep_total
<chr> <dbl>
1 Big brown bat 19.7
2 Thick-tailed opposum 19.4
3 Little brown bat 19.9
4 Giant armadillo 18.1
filter_if能够帮助我们在单个数据维度上进行操作,之前的scoped函数都是在列上进行操作计算。 同时,filter_if()能够结合一些统计计算的函数,包括%in%,between()等。
%>% :: select (name, sleep_total) %>% :: filter (between (sleep_total, 16 , 18 ))
# A tibble: 4 × 2
name sleep_total
<chr> <dbl>
1 Owl monkey 17
2 Long-nosed armadillo 17.4
3 North American Opossum 18
4 Arctic ground squirrel 16.6
%>% filter_all (all_vars (. > 150 ))
[1] mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
<0 rows> (or 0-length row.names)
all_vars(.)能够用于帮助我们对所有的数据超过或不超过等条件进行筛选。any_vars()能够对所有数据凡是满足条件即保留。
group_by函数
%>% dplyr:: group_by (cyl)
# A tibble: 32 × 11
# Groups: cyl [3]
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 21 6 160 110 3.9 2.62 16.5 0 1 4 4
2 21 6 160 110 3.9 2.88 17.0 0 1 4 4
3 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.32 18.6 1 1 4 1
4 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.22 19.4 1 0 3 1
5 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.44 17.0 0 0 3 2
6 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.46 20.2 1 0 3 1
7 14.3 8 360 245 3.21 3.57 15.8 0 0 3 4
8 24.4 4 147. 62 3.69 3.19 20 1 0 4 2
9 22.8 4 141. 95 3.92 3.15 22.9 1 0 4 2
10 19.2 6 168. 123 3.92 3.44 18.3 1 0 4 4
# … with 22 more rows
列名清理
数据框的列名,不要用有空格和中文。 如果拿到的原始数据中列比较多,手动修改麻烦,可以使用janitor::clean_names()函数。
library (readxl)library (janitor) # install.packages("janitor")
Attaching package: 'janitor'
The following objects are masked from 'package:stats':
chisq.test, fisher.test
缺失值处理
library (purrr)<- as_tibble (airquality)%>% purrr:: map (~ sum (is.na (.)))
$Ozone
[1] 37
$Solar.R
[1] 7
$Wind
[1] 0
$Temp
[1] 0
$Month
[1] 0
$Day
[1] 0
%>% :: map_df (~ sum (is.na (.)))
# A tibble: 1 × 6
Ozone Solar.R Wind Temp Month Day
<int> <int> <int> <int> <int> <int>
1 37 7 0 0 0 0
缺失值替换
%>% mutate_all (funs (replace (., is.na (.), 0 )))
Warning: `funs()` was deprecated in dplyr 0.8.0.
ℹ Please use a list of either functions or lambdas:
# Simple named list: list(mean = mean, median = median)
# Auto named with `tibble::lst()`: tibble::lst(mean, median)
# Using lambdas list(~ mean(., trim = .2), ~ median(., na.rm = TRUE))
# A tibble: 153 × 6
Ozone Solar.R Wind Temp Month Day
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 41 190 7.4 67 5 1
2 36 118 8 72 5 2
3 12 149 12.6 74 5 3
4 18 313 11.5 62 5 4
5 0 0 14.3 56 5 5
6 28 0 14.9 66 5 6
7 23 299 8.6 65 5 7
8 19 99 13.8 59 5 8
9 8 19 20.1 61 5 9
10 0 194 8.6 69 5 10
# … with 143 more rows
参考资料
https://bookdown.org/wangminjie/R4DS/tidyverse-dplyr-adv.html#across%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0-1